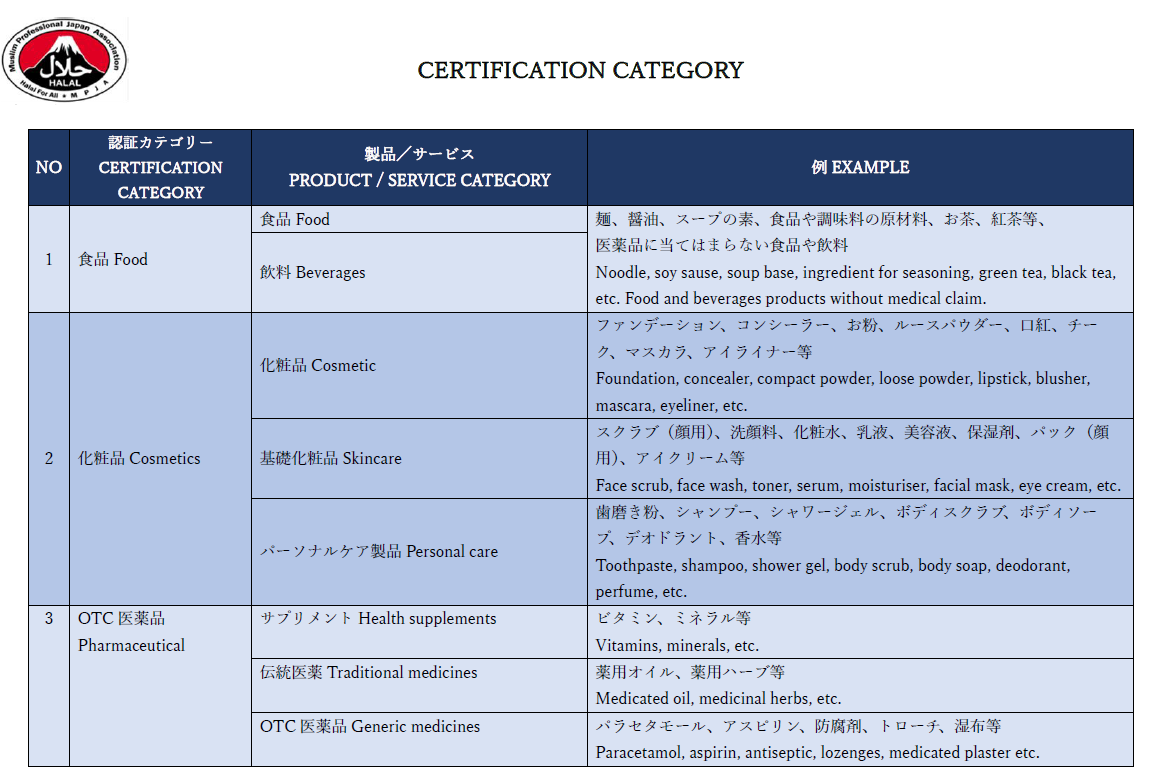
Food/Food Ingredients/Beverages
Foods and beverages are the most commonly known scopes for halal certification. For example, curry sold at general food stores often bears a halal certification mark.
What is less commonly known is that this halal certification mark is not only related to the non-use of “pork”, “alcohol” and “non-halal meat” in the ingredient label but for all ingredients in the ingredient list. However, it indicates that “pork-derived”, “alcohol-derived”, and “non-halal-derived” are not included as ingredients. Therefore, the part that becomes extremely important in the process of halal certification is the halal nature of food raw materials, including food additives.
Depending on the raw material, most of the ingredients available in Japan may be derived from pork and non-halal meat, and even well-known examples include “shortening,” “lard,” and “gelatin.” In order to obtain halal certification, it is necessary to remove such raw materials, replace them with foodstuffs that maintain halal properties (fish, etc.), or replace them with similar raw materials that have already obtained halal certification. We can also introduce food raw materials and additives that have already obtained halal certification, so please contact us.
Cosmetics/Cosmetic Ingredients
Although not common in Japan, halal certification is becoming widespread in Malaysia and Indonesia for products that are indirectly ingested or come into contact with humans other than food. The most typical one is cosmetics, and halal certification is also applied to the cosmetic raw materials that make up them. Familiar examples range from perfumes, skin cosmetics, and lipsticks to medicinal ones such as toothpaste and soap. MPJA has many achievements in halal certification for cosmetics and cosmetic raw materials .
Pharmaceutical
Under this category, pharmaceutical products shall be approved by the relevant authority (drug control authority) in the form of finished dosages for human use. These include health supplements, OTC medicines and traditional medicines. These are drugs that can be purchased without a prescription because they are deemed safe for use without direct medical supervision. Each type of product may have specific regulatory requirements and considerations, but the key principle is to ensure that pharmaceutical products are halal and safe before they reach consumers and patients.
The pharmaceutical certification category is developed in a way that comply with the requirements of halal and GMP for medicinal products. This approach also supports transparency and accountability within the pharmaceutical industry, ultimately benefiting both manufacturers and consumers.
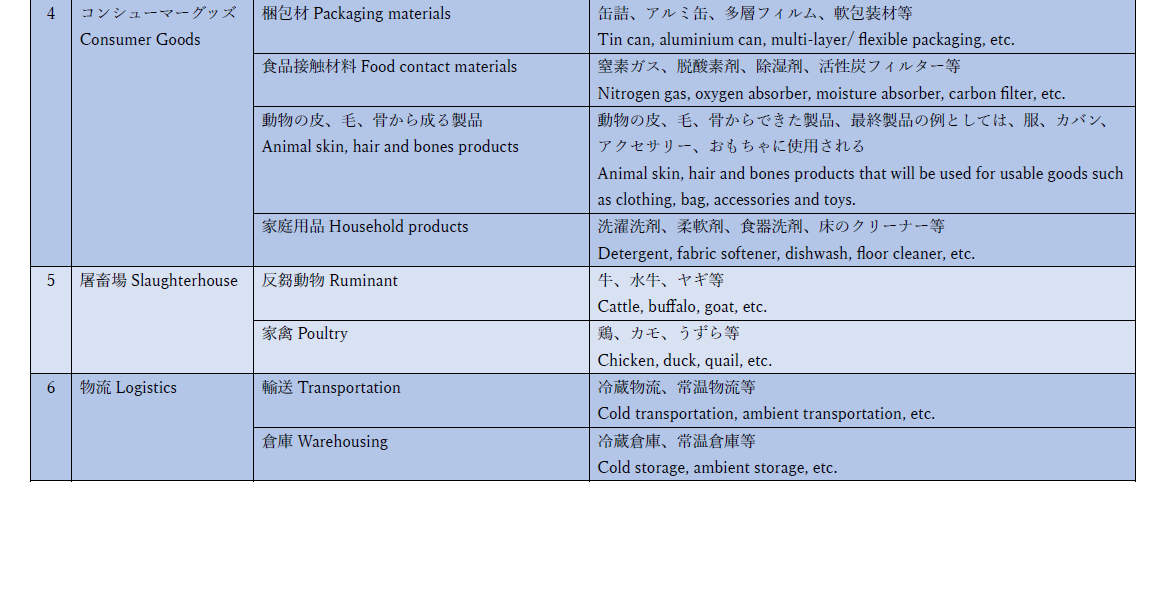
Consumer Goods
Consumer Goods certification category is a certification for finished goods and semi-finished goods which may offer benefits to consumers other than food, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals products that meet the criteria set by MPJA and relevant authority.
This certification category could encompass a wide range of products, including packaging materials (primary packaging), household products, animal-based products (hair, skin and bone), chemicals (for potable water treatment) and other food contact materials. These products may not directly fall into the traditional categories of food, cosmetics or pharmaceuticals, but they play a crucial role in delivering these goods to consumers. Having a certification category specifically tailored to these types of consumer goods acknowledges their importance in the market and ensures that they meet the necessary halal standards for consumer satisfaction and necessity.
Slaughterhouse
Halal certification for slaughterhouse has been significantly increased in the past ten years. Thanks to the husstles made by owners and workers at slaughterhouse, we have halal wagyu available in Japanese market and abroad. The demand for wagyu is uprising still and the expansion of the market does not stop. We have scope for halal slaughterhouse and has been certifying for a number of years. Not only beaf, chicken, duck, and other halal animals are in our scope. To be halal certified, you will have to go through not only our audit but the exporting countries. We have quite enough experiences in certifying slaughterhouse that our skills and knowledge will surely help your certification process smooth.
Logistics
The most ideal halal certification system is a halal guarantee that covers all stages of the supply chain, from the procurement and delivery of raw materials, which is the first stage of the manufacturing process, to the delivery of goods to consumers. To complete this, logistics halal certification is being built as an emerging field. MPJA is currently making ongoing adjustments to provide halal certification to transportation and warehousing companies. Please contact us if you are looking for halal certification for logistics.
Eatery/Hotels
MPJA Muslim Friendly Certification has the advantage of being endorsed by Department of Islamic Development Malaysia (JAKIM) and recognized by the Malaysian Halal certification authority, while being adapted to the Japanese environment.
We have intensive training for workers at the restaurants and it will reflect on the services they can offer to Muslim customers. Please feel free to visit and enjoy food at the restaurants and lodging establishments we certified.
For Muslim-Friendly “MPJA Muslim Friendly Certification”.
For Certified Products detail “click here”.

If you have any question, please feel free to contact us from “Here”.



