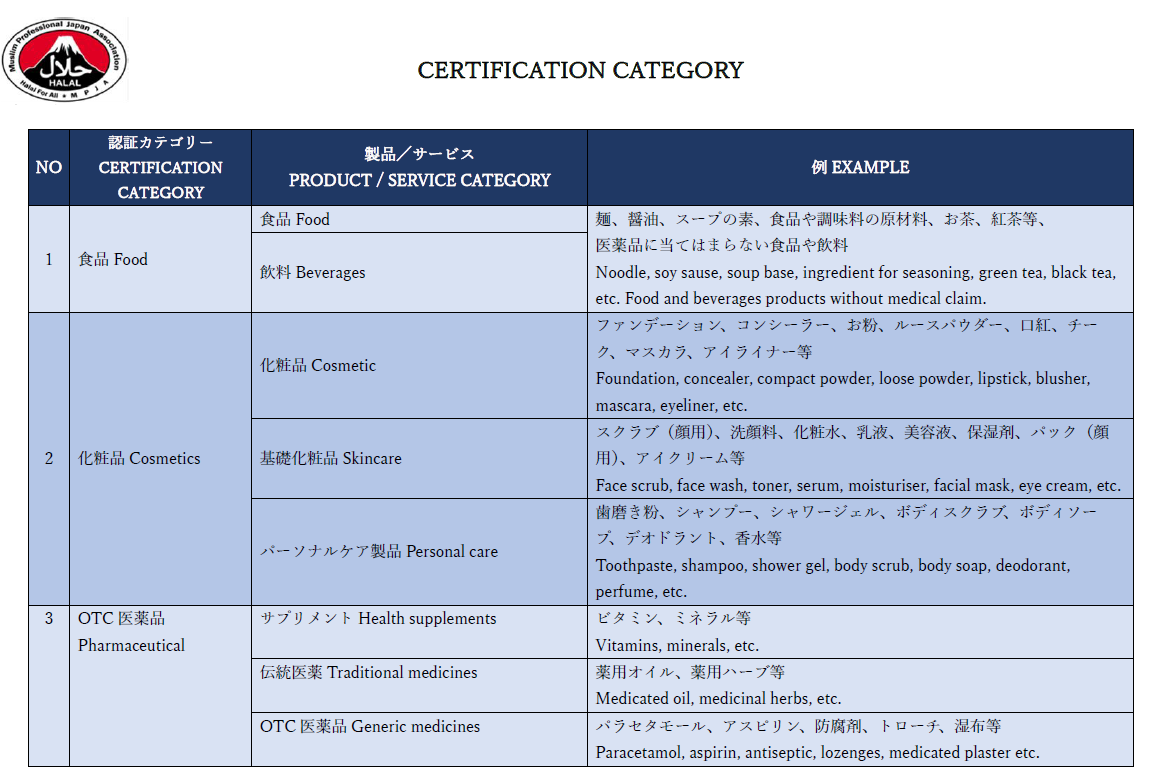
食品/食品原料/飲料
ハラール認証を行う対象として最も一般的に知られているのが食品や飲料となります。
例えば、一般的な食品店で売られているカレーにハラール認証マークが記されていることなどがよくあります。あまり一般的に知られていないこととしては、このハラール認証マークは原材料表示欄における「豚肉」「アルコール」「非ハラール肉」の不使用のみに関わるものではなく、原材料表のすべての材料に対しても、成分として「豚肉由来のもの」「アルコール由来のもの」「非ハラール肉由来のもの」が含まれていないことを示すものです。よって、ハラール認証の過程で極めて重要になってくる部分が、食品添加物なども含めた食品原材料のハラール性となります。
原材料によっては、日本で入手するほとんどのものが豚・非ハラール肉由来のものである場合があり、よく知られている例だけでも、「ショートニング」「ラード」「ゼラチン」といったものがあります。ハラール認証を取得するに当たって、このような原材料は抜くか、ハラール性が保たれる食材(魚など)に代替するか、ハラール認証を取得した同様の原材料への交換が求められます。ハラール認証を取得している食品原材料や添加物をお求めの場合は上記のお問い合わせからご連絡ください。
化粧品/化粧品原料
日本では一般的ではありませんが、マレーシアやインドネシアでは、食品以外でも人間が間接的に摂取する、または人体に触れる製品に対するハラール認証が普及しつつあります。最も代表的なものとして、化粧品があり、更にそれを構成する化粧品原料に対してもハラール認証が行われています。身近な例としては、香水、皮膚用化粧品、口紅といったものから、歯磨き粉や石鹸など薬用のものまであります。化粧品や化粧品原材料へのハラール認証にて、MPJAは数多くの実績があります。
OTC医薬品
このカテゴリーでは、ハラールとGood Manufacturing Practice (GMP)の要件を満たすもので、人が使用する医薬品などが含まれます。これらの製品は、関連する各機関によって承認される必要があり、具体的には健康補助食品、OTC(処方箋なしで購入可能な)薬、薬用のハーブや油などが含まれています。製品が消費者や患者に届く前に、ハラールであることと安全性が保障されている必要があるため、各製品タイプによって異なる特定の規制要件を考慮する必要があります。透明性や信頼性を重視し、製造業者と消費者の両方に利益をもたらすことを目指しています。
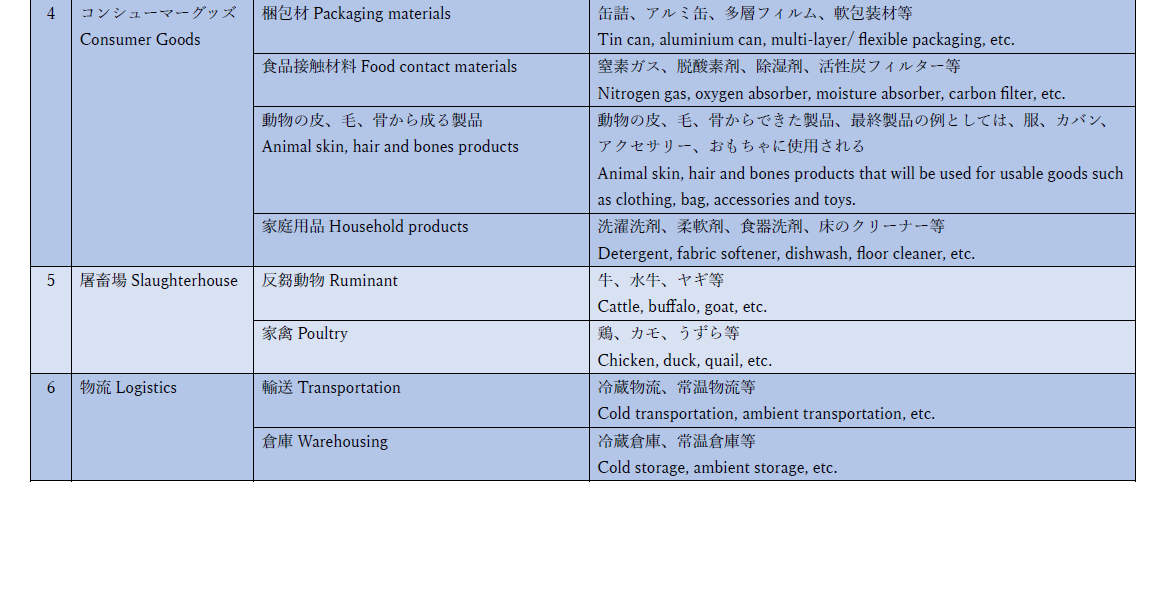
コンシューマーグッズ
コンシューマーグッズカテゴリーは、MPJAおよびハラールに関連する機関が設定した基準を満たし、食品、化粧品、医薬品以外の製品のための認証です。
この認証カテゴリーは、一次包装材料、家庭用品、動物性製品(毛髪、皮膚、骨)、飲料水処理用の化学薬品、およびその他の食品接触材料を含む、幅広い製品を対象とすることができます。これらの製品は、直接的には従来の食品、化粧品、医薬品のカテゴリーには該当しない可能性もありますが、これらの商品を消費者に届ける上で重要な役割を果たしています。このようなコンシューマーグッズに特化した認証カテゴリーが存在することで、消費者の安心のためのハラール基準を満たすことが保証されます。
屠畜場
屠畜場におけるハラール認証はここ10年間で大きく進展しました。皆様のハラールに対するご理解と屠畜場の経営者や従業員達の努力のおかげで、ハラール和牛の人気が国内に留まらず海外にまでおよび始めています。特にマレーシア、インドネシアなどのアジア諸国や海外の富裕層が多い国々での和牛人気は依然として高まっており、和牛ビジネスは拡大し続けているのが現状です。弊協会はハラール認証対象として屠畜場もここ数年間認証を行っており、認証範囲は牛肉のみではなく、鶏肉やアヒル肉、ヤギ肉やそれ以外にも認証を行っています。ハラール認証を取得するためには、弊協会の監査だけでなく、輸出先の国からも審査を受ける必要があり、その際弊協会は屠畜場の認証に関する豊富な経験と実績を持ちあわせているため、認証プロセスを円滑に進めるための知識と知恵を提供することが可能です。
物流
最も理想的なハラール認証システムは、製造工程の最初の段階である原材料の調達・搬入から、商品が消費者の手に届くに至るまで、サプライチェーンのすべての段階をカバーするハラール保証であると言えます。これを完成するものとして、製品の輸送や保管を行う倉庫など物流のハラール認証が新興分野として構築されつつあります。弊協会では現在、運送・倉庫事業者へのハラール認証提供に向けて調整を行っております。
飲食店/宿泊施設
レストランなどの飲食店や、ホテル内のレストランを含めた宿泊施設へのハラール認証は、すでに日本でもインバウンド対応として大々的に行われてきました。飲食店や宿泊施設へのハラール認証において重要な点として、施設内での非ハラール食材・アルコールの提供が原則禁止される、ムスリム従業員の雇用が求められるといった条件が存在します。日本では、このような極めて厳しい基準を満たせるものは中東・北アフリカ・南アジアなどのエスニック料理店や、ムスリム対応に特化した店などに限られてきます。
よってMPJAでは、日本の環境に合わせ、飲食店/宿泊施設のみに対しハラール認証より基準を緩めた形で「ムスリムフレンドリー認証」という制度を確立しています。この「MPJAムスリムフレンドリー認証」を利用することで、施設内での区分けが徹底していることを条件として、アルコールも含めた非ハラール食材の提供が可能であり、またムスリム従業員の雇用は義務化されていません。「MPJAムスリムフレンドリー認証」の特徴として、マレーシア・イスラム開発庁(JAKIM)の推薦を得ており、日本の環境に適合させつつ、マレーシアのハラール認証機関にも認められているという強みがあります。

以上の説明に関して何か疑問や質問がございましたら、些細なことでもお気軽にこちらのお問い合わせからご連絡ください。



